F28ED-NSS-Bot

Used-Centered Experimental Design - F28ED (2020-2021)
Analysis of the degree to which men and women like traditional news and news based on interest.
Group 117 : Yu Hao; Yuxuan Sun; Junhao Song

Abstract.
The experiment presented a study investigating the expressiveness of the robot, the robot showed two kinds of news, one new showed in a traditional way, the others new showed by user preferences. Preliminary results show that in the investigating, the traditional news had the closed result with the news by user interests. In the comparison, the male rated the news more strictly. At the same time, the news that depends on user interests score is relatively fewer than the traditional news.
1. Introduction
News is information about current events. This may be provided through many different media: word of mouth, printing, postal systems, broadcasting, electronic communication, or through the testimony of observers and witnesses to events. Common topics for news reports include war, government, politics, education, health, the environment, economy, business, fashion, and entertainment, as well as athletic events, quirky or unusual events. Government proclamations, concerning royal ceremonies, laws, taxes, public health, and criminals, have been dubbed news since ancient times. [1]
Traditional news mainly refers to the newspaper in this kind of dissemination way. The information is evenly distributed over one page of the newspaper. Relatively speaking, this distribution makes the information coverage of readers more extensive. But, some people also think those news are useless to them and it is a waste of time. Relative to new media, its propagation speed is a little slow. [2]
With the development of The Times and technology, the news also changed ways of distribution [3], such as the app in the mobile phone. By the support of big data algorithms, those apps can push personalized news based on their browsing time and browsing history. It can save customers’ time to find the news they are interested in in the news ocean. But some people also worried about this, they said that it may cause the Information cocoon room effect. [4]
The Problem Space: The both of these approaches have their own advantages. Different people may see things quite differently. Some people think that reading traditional news is a waste of time. However, some people think that it is an invasion of privacy to send news according to their interests. So, this research decided to study the views of different groups on these two approaches.
Conceptual Design: The robot will adjust the news based on the user’s questionnaire, and the interests direction selected by the user in the questionnaire will change the segment captured by the robot. It makes the robot model close to the algorithm of big data of some app. It can meet the study requirements of pushing news according to different people’s interests.
Users and Requirements: The target audience is a wide range of adults, from 18 to 40, regardless of education and gender. Our subject pool is made up of these ideal end-users. Our application addressed all of the requirements listed.
– F-01 The user must be able to interact with the computer.
– F-02 The user must be able to interact with the new websites.
– F-03 The robot must be able to gauge the user’s gender.
– F-04 The robot must be able to adapt to the user’s interests.
– F-05 The robot must be able to gauge the user’s score given to the news system.
– NF-01 The robot must be easy to understand,
– NF-02 The robot must react quickly to the user.
Design: In this study, two similar robots were designed, and different robots were given for different batches of users. The number of the same). (i) The 1 robot first gives the news pushed according to the interest, then gives the traditional news. (ii) The robot first gives the traditional news, then gives the news according to the interest push.
The bot gives users several options of interest in the questionnaire, and the robot can change the news from the news website according to these options. For example, If the user chooses to be interested in sports in the questionnaire, the robot will go to the sports section to grab the news push to the user. The user’s choices in the questionnaire will determine the robot’s actions.
The interaction flow is basically fixed, because the design framework is a question and answer or selection form. Basically, unable to handle user initiative. It only can record user suggestions at the end. As shown in Figure 1. The framework will be used for logic and program operation. It was finally launched on the telegram platform.
Figure 1: Use \/start to realize the docking with the telegram platform.
prompts and actions:
– Say hello to the user.
– Jumps to the end when the user refuses to provide information.
– Interrupt questionnaire (when error is reported).
– Exit directly after the time limit.
Prototype for study: The prototype is from a teacher’s example. User Bot Framework Composer to edit the robot.
2. Prior Work
Today, everyone knowed that different groups have different levels of interest in different kinds of news. The younger generation has different needs and attitudes to news from the previous generation. Young people are primarily driven by “development” and “enjoyment” in their lives, and this is reflected in the choices they make when they get news. [5] So traditional news is dead among the young? Not necessarily. Metro, the UK’s free newspaper, is an introduction to millennials, with 44 percent of readers saying they enjoy reading newspapers. “Other newspapers envy us that our audience is mostly young people between the ages of 18 and 35,” metro editor-in-chief TedYoung told the author. And Some of their readers say pop-up ads and pre-rolling ads on digital platforms push them back to traditional news. [6] At the same time,The soaring growth of new media has also raised some concerns, such as information cocoons. Personalized recommendation of news information based on algorithms and big data analysis can to a certain extent relieve our overwhelmedness in the face of massive information. However, it is precisely because of this information recommendation based on individual uniqueness that we are bound to the closed space formed by the constant echo of the same voice. [7]
3. Research Question and Hypotheses
Research question: The research question is about which types of news are more liked by users, and how much men and girls like different types of news.
Hypothesis: Here we list the hypotheses involved in this study and the corresponding null hypotheses.
– H1: Traditional news is more loved by all users than news based on user interests.
Empty hype: Traditional news will not be more popular among all users than news based on user interests.
– H2: News based on user interests is more popular among all users than traditional news.
Empty hype: News based on user interests will not be more popular among all users than traditional news.
– H3: Traditional news is more popular among male users than news based on user interests.
Empty hype: Traditional news will not be more popular among male users than news based on user interests.
– H4: Traditional news is more popular among female users than news based on user interests.
Empty hype: Traditional news will not be more popular among female users than news based on user interests.
– H5: News based on user interests is more popular with male users than traditional news.
Null Hyp: News based on user interests will not be more popular among male users than traditional news.
– H6: News based on user interests is more popular among female users than traditional news.
Null Hyp: News based on user interests will not be more popular among female users than traditional news.
4. Experiment Design
Conditions: There are two conditions. Condition A is News based on user interests. Condition B is Traditional news. This experiment is within subjects. That is, each subject will try to use two types of news for this task.

Figure 2: The robot provides options for users to choose their areas of interest to read.
The Task: In this experiment, it is divided into two groups. The number of subjects in both groups was the same. The first group will be tested with all female subjects. Another group of all male subjects will be tested. Both groups completed reading the two news items at the same time. Finally, each topic chooses their favorite news method. The experiment will consist of three parts. At the beginning, all subjects will fill out a Pre-Questionnaire. The second part divided the subjects into two groups and asked them to read two kinds of news. When reading news based on user interests, the system will provide multiple choices. Let users choose their areas of interest to read. Just like Figure 2. In the third part, the topics need to choose the type of news they like (choose one) through an After-Questionnaire.Finally, users give their favorite news types (out of 10 points).
Variables: The independent variable is the number of men and women. The dependent variable is the number of people who like different news and the score each person gives to the news they like. The collection of data needed for the experiment can be used for research: the number of men and women, and the type of news selected by the subjects. The subject’s rating of the news. Auxiliary data include age, work status, experiment time, educational background and hobbies of reading news.
Confounding Variable: The confounding variable is about the difference between the age of the subject and the native language. So we only require people who are 18 to 40 years old whose mother tongue is English. Another confusing variable is whether the subject has the habit of reading news. The solution will be to have a pre-tested questionnaire to identify the problem and incorporate it into the data analysis.
Questionnaires: The robot asks the participant to fill out a questionnaire before interacting with the participant. The Pre-test questionnaire (age, gender, work or study, highest degree, whether users have the habit of reading news). As shown in Figure 3. Users complete the questionnaire by filling in single-choice questions. After the participant has participated in the experiment, the participant will fill out a simple questionnaire. The After-Questionnaire (the type of news user like, users score for this news). All information in the questionnaire is confidential and not public.

Figure 3: Multiple choice questions in Pre-Questionnaire
5. Data Collection
In this study, the interactive robot is fully automated and successfully deployed through the telegram platform. Therefore, no “The Wizard of Oz” is necessary. The data is collected in accordance with GDPR. No personal sensitive information is obtained from topics other than the subject. Their names are collected and matched with the subject ID. The link information has been kept separate from the data in the locked cabinet of the Microsoft Office form. This means that the data is “anonymous and linked” according to GDPR standards. The collected data is stored on the secure server of the Microsoft Office Form.
There are 20 subjects in total, aged between 18-40 years old, female: 10, male: 10. This is an inter-research study: 4 test subjects prefer traditional news, and 16 test subjects prefer news based on user interests.
6. Analysis
After the data is collected, analyze the collected data, After collecting the data, analyze the collected data, and plot the frequency of men and women with different scores on preferred news, as shown below:
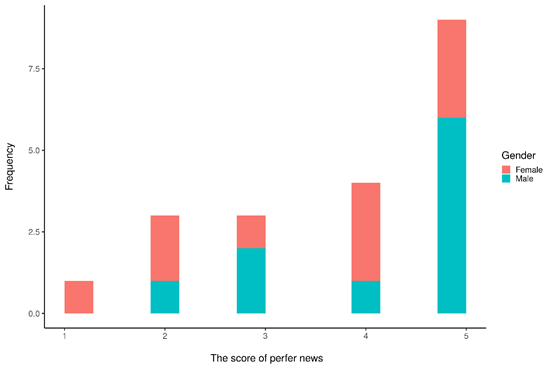
` `Figure 4: Different genders’ score of perfer news
Figure 4 shows that women have an average score for news preference, with more than 50% giving a high score of 4 or 5. For men, the vast majority of men gave a high score of 5 points and no one scored 1 point.
Collect scoring data for different news types and plot them as follows.

` `Figure 5: Proportion of testee data for different news types
In traditional news, half of the people scored 5 points, and no one scored less than two points, but in news based on user interests, although 5 points still accounted for 40%, nearly 20% of them still scored 2 points or less.

` `Figure 6: Different types of score for perfer news
It can be seen from figure 6 that the difference between traditional news and new news is not obvious.
7. Conclusion and Future work
In summary, although there is a slight difference between traditional news and new news as shown in the figure, in the statistical test, the p-value is equal to 0.2423, so there is no significant difference between the calculated data. Finally, it can be concluded that gender has no significant difference in judging different news preferences.

Figure 7: Calculation results of P-value
In future work, the experiment will investigate other aspects, Whether educational background or age is the main factor that users love different news types. Further research can show which characteristics of this example, whether it is reading habits, age, or academic qualifications, contribute the most to the implementation.On the other hand, we should also explore the effectiveness of robots among different users. Corresponding to different groups of people, the impact of robot effectiveness.
8. Appendices
\1. Experimental plan
\2. Experimental protocol
\3. Ethics form
\4. Blank questionnaires
9. References
- J. Stephens, History of News (1988), p. 13.
- K. McNair, Cultural Chaos (2006), pp. 1–2.
- B. Barrett & W. Rantanen, The Globalization of News (1998), p. 6.
- J. Achten, World News Prism (1996), p. 8.
- W. Yuchen, Research on the Influence of new Mainstream Media on the values of youth Groups [J]. News Research Guide, 2020, V. 11;No.185(05):64-66.
- L. Hao, MediaChange, October 16 2017 , p. 12.
- H. Jinbin. Analysis on the Characteristics, Usage habits and Motivation of mobile Internet Users’ News reading [J].Media Forum, 2018, 000(005): p.85-86.
